
Java8 Lambda表达式详解
Lambda表达式介绍
Java 8的一个大亮点是引入Lambda表达式,使用它设计的代码会更加简洁。通过Lambda表达式,可以替代我们以前经常写的匿名内部类来实现接口。Lambda表达式本质是一个匿名函数;
体验Lambda表达式
我们通过一个小例子来体验下Lambda表达式;
我们定义一个计算接口 只有一个方法add;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cal c1=new Cal() {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
};
int c=c1.add(1,2);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
interface Cal{
int add(int a,int b);
}这个是我们以前的实现,匿名内部类,然后调用执行;
我们现在用Lambda表达式改写下:
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cal c1=(int a,int b) ->{return a+b;};
int c=c1.add(1,2);
System.out.println(c);
}
int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
}
interface Cal{
int add(int a,int b);
}匿名内部类,直接改成了:
Cal c1=(int a,int b) ->{return a+b;};
简洁多了;
是不是感觉Lambda表达式挺强大,
接下来我们来看看Lambda表达式的语法吧;
Lambda表达式语法
我们看下这个Lambda表达式:
(int a,int b) ->{return a+b;};
这个本质是一个函数;
一般的函数类似如下:
int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}有返回值,方法名,参数列表,方法体
Lambda表达式函数的话,只有参数列表,和方法体;
( 参数列表 ) -> { 方法体 }
说明:
( ) :用来描述参数列表;
{ } : 用来描述方法体;
-> :Lambda运算符,可以叫做箭头符号,或者goes to
Lambda表达式语法细讲
我们搞一个案例,接口方法参数,无参,单个参数,两个参数,有返回值,没有返回值,这六种情况都罗列下:
interface If1{
/**
* 无参数无返回值
*/
void test();
}
interface If2{
/**
* 单个参数无返回值
* @param a
*/
void test(int a);
}
interface If3{
/**
* 两个参数无返回值
* @param a
* @param b
*/
void test(int a,int b);
}
interface If4{
/**
* 无参数有返回值
* @return
*/
int test();
}
interface If5{
/**
* 单个参数有返回值
* @param a
* @return
*/
int test(int a);
}
interface If6{
/**
* 多个参数有返回值
* @param a
* @param b
* @return
*/
int test(int a,int b);
}我们用Lambda表达式实现:
// 无参数无返回值
If1 if1=()->{
System.out.println("无参数无返回值");
};
if1.test();
// 单个参数无返回值
If2 if2=(int a)->{
System.out.println("单个参数无返回值 a="+a);
};
if2.test(3);
// 两个参数无返回值
If3 if3=(int a,int b)->{
System.out.println("两个参数无返回值 a+b="+(a+b));
};
if3.test(2,3);
// 无参数有返回值
If4 if4=()->{
System.out.print("无参数有返回值 ");
return 100;
};
System.out.println(if4.test());
// 单个参数有返回值
If5 if5=(int a)->{
System.out.print("单个参数有返回值 ");
return a;
};
System.out.println(if5.test(200));
// 多个参数有返回值
If6 if6=(int a,int b)->{
System.out.print("多个参数有返回值 ");
return a+b;
};
System.out.println(if6.test(1,2));运行输出:
无参数无返回值 单个参数无返回值 a=3 两个参数无返回值 a+b=5 无参数有返回值 100 单个参数有返回值 200 多个参数有返回值 3
Lambda表达式精简语法
那件语法注意点:
1,参数类型可以省略
2,假如只有一个参数,()括号可以省略
3,如果方法体只有一条语句,{}大括号可以省略
4,如果方法体中唯一的语句是return返回语句,那省略大括号的同事return也要省略
改写实例:
/**
* @author java1234_小锋
* @site www.java1234.com
* @company Java知识分享网
* @create 2020-08-12 16:43
*/
public class Program2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1,参数类型可以省略
// 2,假如只有一个参数,()括号可以省略
// 3,如果方法体只有一条语句,{}大括号可以省略
// 4,如果方法体中唯一的语句是return返回语句,那省略大括号的同事return也要省略
// 无参数无返回值
If1 if1=()->System.out.println("无参数无返回值");
if1.test();
// 单个参数无返回值
If2 if2=a->System.out.println("单个参数无返回值 a="+a);
if2.test(3);
// 两个参数无返回值
If3 if3=(a,b)->{
System.out.println("两个参数无返回值 a+b="+(a+b));
};
if3.test(2,3);
// 无参数有返回值
If4 if4=()->100;
System.out.println(if4.test());
// 单个参数有返回值
If5 if5=a->{
System.out.print("单个参数有返回值 ");
return a;
};
System.out.println(if5.test(200));
// 多个参数有返回值 参数类型可以省略
If6 if6=(a,b)->a+b;
System.out.println(if6.test(1,2));
}
}方法引用
有时候多个lambda表达式实现函数是一样的话,我们可以封装成通用方法,以便于维护;
这时候可以用方法引用实现:
语法是:对象::方法
假如是static方法,可以直接 类名::方法
实例如下:
public class Program2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方法引用
// 语法:
// static方法 类名::方法名
// 普通方法 对象名::方法名
Program2 program2=new Program2();
If5 if5=program2::test;
If5 if52=Program2::test2;
System.out.println(if5.test(1));
System.out.println(if52.test(1));
}
public int test(int a){
return a-2;
}
public static int test2(int a){
return a-2;
}
}构造方法引用
如果函数式接口的实现恰好可以通过调用一个类的构造方法来实现,
那么就可以使用构造方法引用;
语法:类名::new
实例:
先定义一个Dog实体,实现无参和有参构造方法;
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog() {
System.out.println("无参构造方法");
}
public Dog(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("有参构造方法");
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}在定义两个接口:
interface DogService{
Dog getDog();
}
interface DogService2{
Dog getDog(String name,int age);
}测试:
public class Program3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 普通方式
DogService dogService=()->{
return new Dog();
};
dogService.getDog();
// 简化方式
DogService dogService2=()->new Dog();
dogService2.getDog();
// 构造方法引用
DogService dogService3=Dog::new;
dogService3.getDog();
// 构造方法引用 有参
DogService2 dogService21=Dog::new;
dogService21.getDog("小米",11);
}
}执行结果:
无参构造方法 无参构造方法 无参构造方法 有参构造方法
综合实例
下面我们通过一个lambda操作集合的综合实例,来深入体验下Lambda表达式用法;
public class Program4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Dog> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Dog("aa",1));
list.add(new Dog("bb",4));
list.add(new Dog("cc",3));
list.add(new Dog("dd",2));
list.add(new Dog("ee",5));
// 排序
System.out.println("lambda集合排序");
list.sort((o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge());
System.out.println(list);
// 遍历集合
System.out.println("lambda遍历集合");
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}运行输出:
lambda集合排序
[Dog{name='aa', age=1}, Dog{name='dd', age=2}, Dog{name='cc', age=3}, Dog{name='bb', age=4}, Dog{name='ee', age=5}]
lambda遍历集合
Dog{name='aa', age=1}
Dog{name='dd', age=2}
Dog{name='cc', age=3}
Dog{name='bb', age=4}
Dog{name='ee', age=5}我们来分析下集合的sort方法,
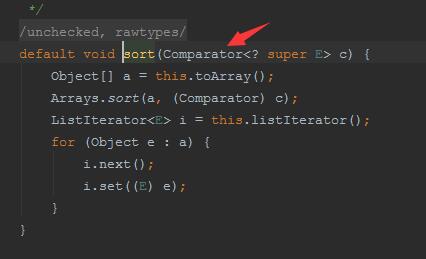
sort方法里有一个Comparator接口,再点进去看下:
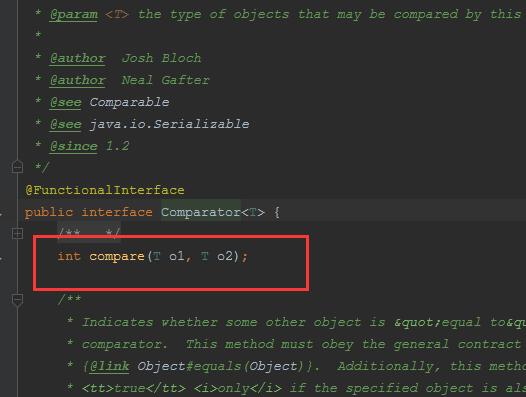
我们通过lambda就可以轻松实现排序:
(o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge()
再看下集合的forEach方法,点进去:

有个消费者Consumer接口,再点进去:

接口里有个接口参数的accept的方法;
所以我们直接方法引用 直接输出每次的遍历值即可;
System.out::println
@FunctionalInterface注解
前面我们会发现Consumer接口,Comparator接口都有
@FunctionalInterface注解;
这个注解是函数式接口注解,所谓的函数式接口,当然首先是一个接口,然后就是在这个接口里面只能有一个抽象方法。
这种类型的接口也称为SAM接口,即Single Abstract Method interfaces
特点
接口有且仅有一个抽象方法
允许定义静态方法
允许定义默认方法
允许java.lang.Object中的public方法
该注解不是必须的,如果一个接口符合"函数式接口"定义,那么加不加该注解都没有影响。加上该注解能够更好地让编译器进行检查。如果编写的不是函数式接口,但是加上了@FunctionInterface,那么编译器会报错
实例
// 正确的函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TestInterface {
// 抽象方法
public void sub();
// java.lang.Object中的public方法
public boolean equals(Object var1);
// 默认方法
public default void defaultMethod(){
}
// 静态方法
public static void staticMethod(){
}
}
// 错误的函数式接口(有多个抽象方法)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TestInterface2 {
void add();
void sub();
}系统内置函数式接口
Java8的推出,是以Lambda重要特性,一起推出的,其中系统内置了一系列函数式接口;
再jdk的java.util.function包下,有一系列的内置函数式接口:
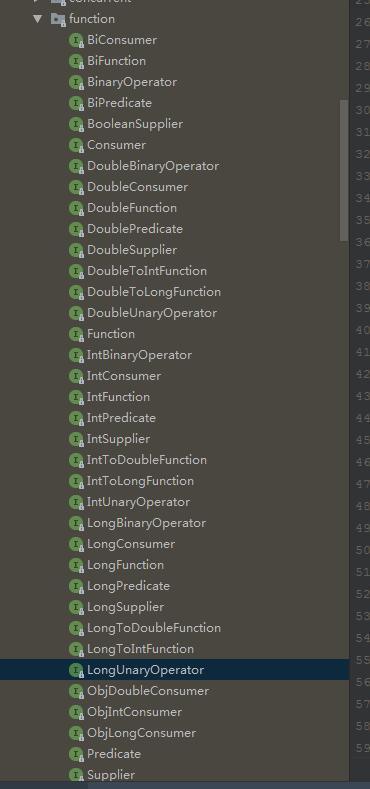
比如常用的Consumer,Comparator,Predicate,Supplier等;


- Java核心基础(145)
- Mysql(2)
- Docker(35)
- Dubbo(7)
- 007项目(0)
- SVN(22)
- QQ第三方登录(6)
- mybatis-plus(20)
- Mycat(30)
- Layui(2)
- 微信扫码登录(4)
- Git(50)
- SpringCloud(33)
- Tomcat(6)
- 支付宝接口(3)
- NodeJs(1)
- IDEA(24)
- SpringBoot(11)
- Nginx(24)
- Vue.js(50)
- jsoup(6)
- shiro(1)
- hibernate(1)
- EhCache缓存框架(4)
- webservice(10)
- CAS单点登录(7)
- elasticsearch(31)
- Redis(17)
- maven(6)
- 活动(20)
- centos(25)
- log4j日志(8)
- IT之路(26)
- activiti(26)
- 随心生活(19)
- java爬虫技术(14)
- 网站SEO(2)
- httpclient(7)
- htmlunit(10)
- 2026年01月(1)
- 2021年10月(1)
- 2021年02月(3)
- 2020年11月(3)
- 2020年10月(4)
- 2020年09月(7)
- 2020年08月(18)
- 2020年07月(21)
- 2020年06月(37)
- 2020年05月(17)
- 2020年04月(12)
- 2020年03月(10)
- 2020年02月(14)
- 2020年01月(12)
- 2019年12月(15)
- 2019年11月(27)
- 2019年10月(5)
- 2019年09月(1)
- 2019年08月(4)
- 2019年07月(28)
- 2019年06月(16)
- 2019年05月(4)
- 2019年04月(3)
- 2019年03月(2)
- 2019年02月(7)
- 2019年01月(20)
- 2018年12月(2)
- 2018年11月(5)
- 2018年10月(30)
- 2018年09月(11)
- 2018年08月(5)
- 2018年07月(9)
- 2018年06月(4)
- 2018年05月(4)
- 2018年04月(3)
- 2018年03月(7)
- 2018年02月(6)
- 2018年01月(13)
- 2017年12月(3)
- 2017年11月(10)
- 2017年10月(1)
- 2017年09月(9)
- 2017年08月(12)
- 2017年07月(19)
- 2017年06月(21)
- 2017年05月(1)
- 2017年04月(12)
- 2017年03月(13)
- 2017年02月(12)
- 2017年01月(14)
- 2016年12月(8)
- 2016年11月(25)
- 2016年10月(16)
- 2016年09月(13)
- 2016年08月(20)
- 2016年07月(12)
- 2016年06月(36)
- 2016年05月(10)
- 2016年04月(19)
- 2016年03月(14)
- 2016年02月(23)
- 2016年01月(1)